Ever wondered what those seemingly insignificant digits on your credit card are actually for? They're your first line of defense against the ever-present threat of online fraud. In the digital age, protecting your financial information is more critical than ever. One of the most important tools in this fight is the Card Verification Value, or cvv.
The cvv, a seemingly simple three- or four-digit security code, plays a pivotal role in safeguarding your credit card information during online transactions. But what exactly is a cvv, and how does it work to protect you from fraud? This seemingly small number adds a layer of security, ensuring that only you, the cardholder, can use your card for online purchases.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition of cvv | A security code, usually three or four digits, found on the back or front of your credit or debit card. It verifies the cardholder's access to the physical card during online transactions. |
| Alternate Names | cvc (Card Verification Code), csc (Card Security Code), cvn (Card Verification Number), cid (Card Identification Number – primarily used by American Express). |
| Purpose | To prevent credit card fraud in "card-not-present" transactions, such as online purchases. It helps verify that the person making the purchase has physical possession of the card. |
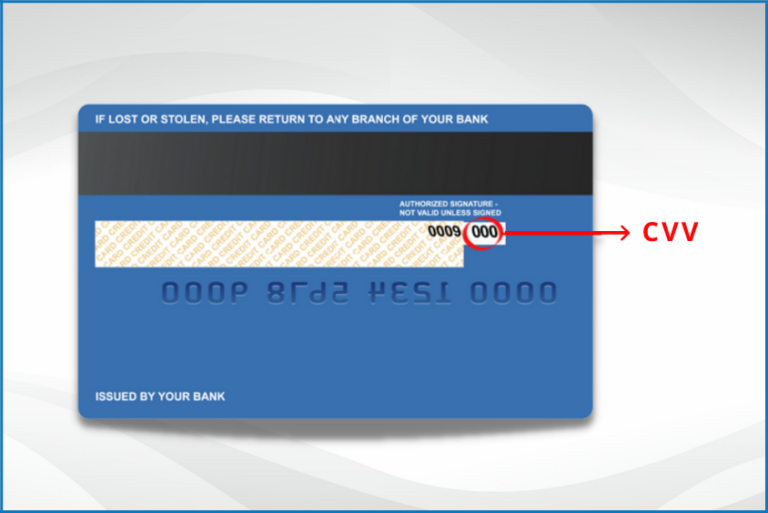
| Location | Typically found on the back of Visa and Mastercard cards. On American Express cards, it's usually on the front. |
| Number of Digits | Usually three digits for Visa and Mastercard, and four digits for American Express. |
| Security Importance | Crucial for online security. Merchants are generally prohibited from storing cvv numbers, so if a hacker steals your card number, they still need the cvv to make online purchases. |
| How it Works | When you enter your cvv during an online purchase, the merchant sends it to the card issuer for verification. If the cvv matches the one on file, the transaction is approved. |
| Difference from PIN | A cvv is different from a PIN (Personal Identification Number). A PIN is used for in-person transactions at ATMs or point-of-sale terminals, while the cvv is used for online or phone transactions. |
| Best Practices |
|
| Industry Standards | The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) prohibits merchants from storing cvv numbers after a transaction. |
Think of the cvv as the digital equivalent of a signature. It's a way for merchants to confirm that you, the cardholder, are actually making the purchase. Without it, anyone who has your card number could potentially use it for unauthorized transactions. This is why protecting your cvv is of utmost importance.
So, what exactly does "cvv" stand for? It stands for "Card Verification Value." However, depending on the card issuer, you might encounter it under different names. These include cvc (Card Verification Code), csc (Card Security Code), cvn (Card Verification Number), or even cid (Card Identification Number), particularly for American Express cards. Regardless of the acronym, the function remains the same: to provide an extra layer of security for your credit card transactions.
The primary function of cvv numbers is to enable online merchants to verify that the person making the purchase has physical access to the credit card. By requiring the cvv at the time of purchase, merchants can significantly reduce the risk of fraudulent transactions. This is especially crucial in today's digital landscape, where online shopping is prevalent and the risk of credit card theft is ever-present.
Banks and credit card issuers rely on the cvv to minimize fraudulent digital transactions. When you enter your cvv during an online purchase, it's transmitted securely to your card issuer for verification. If the entered cvv matches the one on file, the transaction is approved. This process adds an extra layer of authentication, making it much harder for fraudsters to use stolen credit card information.
While most credit and debit cards have two cvvs, only one is typically used for online purchases. The first cvv is often encoded in the magnetic strip on the back of the card, used for in-person transactions. The second cvv, the one you're usually asked to provide online, is printed on the card itself. This separation of cvvs further enhances security, as even if a thief manages to skim your card information from the magnetic strip, they still won't have access to the cvv needed for online purchases.
Understanding what a cvv is, where to find it, and how it protects your finances from fraud is crucial in today's world. It's a simple yet powerful tool that helps prevent unauthorized transactions and safeguards your hard-earned money. By taking the necessary precautions, such as never sharing your cvv and only entering it on secure websites, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of credit card fraud.
The cvv serves as an additional layer of security for your credit card, acting as a deterrent to potential fraud. It's a unique identifier that confirms you have physical possession of the card, making it more difficult for criminals to use stolen card information for online purchases. This simple measure can save you from significant financial losses and the hassle of dealing with fraudulent charges.
It's important to remember that a cvv is different from the PIN associated with your credit card. Your PIN is used for in-person transactions at ATMs or point-of-sale terminals, while the cvv is specifically designed for online or phone purchases. This distinction is important to understand, as you should never share your PIN with anyone online, as it's not required for these types of transactions.
In essence, the purpose of a cvv is to provide an extra layer of protection against potential fraud. It's a security measure that helps ensure that only you, the authorized cardholder, can use your credit card for online transactions. By requiring this code, merchants can minimize the risk of accepting fraudulent payments and protect themselves and their customers from financial losses.
So, where can you find your cvv? The location of the cvv varies depending on the card issuer. For Visa and Mastercard credit cards, it's typically a three-digit code located on the back of the card, usually near the signature strip. For American Express cards, the cvv is generally a four-digit code printed on the front of the card, above the embossed card number.
Different card issuers may use slightly different names and locations for cvvs. While the term "cvv" is widely recognized, you might encounter other terms like "cvc" or "csc." Regardless of the name, the function remains the same: to verify your identity as the cardholder during online transactions. Always familiarize yourself with the specific location of the cvv on your card to avoid confusion when making online purchases.
In this digital era, where online transactions are commonplace, a cvv, or card verification value, plays a pivotal role in your financial security. It may seem like just another set of numbers on your credit or debit card, but it's a critical component in preventing unauthorized purchases and safeguarding your personal information.
cvv codes are designed to help prevent unauthorized transactions on your credit card. By requiring this code during online purchases, merchants can verify that you have physical possession of the card and reduce the risk of accepting fraudulent payments. This simple measure can provide significant peace of mind, knowing that your credit card is better protected against misuse.
While your credit card number may be stored by certain retailers, storing the cvv is strictly against credit card compliance standards. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) prohibits merchants from storing sensitive cardholder data, including the cvv. This regulation is in place to protect consumers from potential data breaches and unauthorized access to their financial information.
If an identity thief manages to hack a retailer's system and obtain your credit card number, they could still be prevented from making purchases online or over the phone if they don't have your cvv. This is because the cvv is not stored by most merchants, making it difficult for criminals to use stolen card numbers for fraudulent transactions. This highlights the importance of the cvv as an added layer of security for your credit card.
Credit card cvvs (card verification values) act as an additional layer of security for protection against fraud. They provide an extra level of authentication, ensuring that only authorized cardholders can use their cards for online purchases. This measure helps protect both consumers and merchants from financial losses resulting from fraudulent transactions.
Always exercise caution when providing your cvv. Never share it with anyone over the phone, email, or any other unsecure channel. Only enter your cvv on secure websites when making online purchases. Look for the "https" in the website address and a padlock icon in your browser's address bar to ensure that the website is using encryption to protect your data.
Avoid sharing photos of your credit card online. Posting images of your credit card on social media or any other public platform can expose your card number, expiration date, and cvv to potential fraudsters. This information can be used to make unauthorized purchases, so it's essential to keep your credit card information private and secure.
Never send your cvv via email, text, or other unsecured channels. These communication methods are not secure and can be easily intercepted by hackers. Always be cautious about sharing sensitive information online and only provide your cvv on secure websites when making a purchase.
Only provide credit card information when you're on a secured internet connection. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks when making online purchases, as these networks are often unsecured and can be vulnerable to hacking. Use a private, password-protected Wi-Fi network or your mobile data connection to ensure that your data is protected during transmission.
The cvv serves as a security code to prevent fraud and reduce unauthorized transactions. It's a simple yet effective tool that helps protect your credit card from misuse. By understanding how the cvv works and taking the necessary precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of credit card fraud.
The cvv is also known as several other acronyms in the industry, including cvc, csc, cvn, and cid. While the terminology may vary, the purpose remains the same: to provide an extra layer of security for your credit card transactions.
The credit card industry is continually working to find new and innovative ways to ensure that hackers can't take advantage of credit card holders. As technology evolves, so do the methods used by fraudsters to steal credit card information. The industry is constantly developing new security measures to stay one step ahead of the criminals.
One company working on the issue is Idemia, formerly Oberthur Technologies, a digital payment and security startup based in France. Idemia is developing advanced security solutions to protect credit card data and prevent fraud. These solutions include biometric authentication, tokenization, and other cutting-edge technologies.
On Visa and Mastercard credit cards, the cvv is typically located on the back of the card, near the signature strip. It's a three-digit code that's printed, not embossed, on the card. This code is used to verify your identity during online and phone transactions.
The credit card industry is continually working to find new and innovative ways to ensure that hackers can't take advantage of credit card holders. As technology evolves, so do the methods used by fraudsters to steal credit card information. The industry is constantly developing new security measures to stay one step ahead of the criminals.
One company working on the issue is Idemia, formerly Oberthur Technologies, a digital payment and security startup based in France. Idemia is developing advanced security solutions to protect credit card data and prevent fraud. These solutions include biometric authentication, tokenization, and other cutting-edge technologies.
The cvv (sometimes referred to as a cid) on credit cards adds an extra layer of protection when you're making a purchase online or over the phone since it's harder to prove you're the cardholder. This is because the cvv is not stored by most merchants, making it difficult for criminals to use stolen card numbers for fraudulent transactions.
If a thief has your card information, they won't have the cvv unless they also have the physical card. This is because the cvv is not typically stored by merchants or transmitted over unsecure networks. This makes it difficult for criminals to use stolen card numbers for online purchases without the cvv.
cvv2 stands for "Card Verification Value 2," cvc2 stands for "Card Validation Code 2," and cid (Card Identification Number, for American Express) are values that are used as a security feature for verifying your credit card while making "card not present" transactions. These codes are essential for protecting your credit card information during online purchases.
Ultimately, safeguarding your cvv is the most crucial step you can take to ensure the security of your credit card. By keeping your cvv safe and secure, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of credit card fraud.
To summarize, the following are some of the recommended steps to accomplish that goal:
- Do not write down the cvv;
- Do not share the cvv, even with a colleague at work;
- Scan your statement frequently to identify any unauthorized charges, and store your actual credit card securely.
The cvv number of your debit or credit card is typically located on the backside of the card. It's usually a three-digit code that's printed near the signature strip. However, for American Express cards, the cvv is located on the front of the card.
Sometimes, the cvv is printed on the front side of the card, but you will usually find it on the backside. Always check both sides of your card to locate the cvv before making an online purchase.
Technically speaking, cvv2 and cvv refer to the same thing: they are both security codes that are used to verify your credit card during online transactions. The "2" in cvv2 simply indicates that it's the second version of the code.
cvv is an umbrella term that covers all the variations of card verification codes, including cvc, csc, cvn, and cid. While the terminology may vary, the purpose remains the same: to provide an extra layer of security for your credit card transactions.
Every credit card has a card security code printed on it. This code is used to verify your identity during online and phone transactions. Without this code, it would be much easier for fraudsters to use stolen card numbers for unauthorized purchases.
Both debit and credit cards have cvv codes, which can be found either on the front or the back of the card. Always familiarize yourself with the location of the cvv on your card to avoid confusion when making online purchases.
cvc stands for card verification code and is essentially the same as cvv. Both terms refer to the security code that's used to verify your credit card during online transactions.
Different card issuers have different names for it, but it serves the same purpose — to confirm your transactions. Regardless of the terminology used, the function remains the same: to provide an extra layer of security for your credit card transactions.
A credit card’s cvv acts as another line of security against fraud. It makes it more difficult for criminals to use stolen card numbers for online purchases.
The cvv, or card verification value, can also be referred to as the csc, or card security code. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the security code that's used to verify your credit card during online transactions.
Understanding how the cvv on your credit card or debit card protects against fraud is crucial in today's digital world. By taking the necessary precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of credit card fraud.
Knowing where your cvv can be found on your card is essential for making online purchases. Always check both sides of your card to locate the cvv before entering it on a website.
A card security code (csc; also known as cvc, cvv, or several other names) is a series of numbers that, in addition to the bank card number, is printed (but not embossed) on a credit or debit card. This code is used to verify your identity during online and phone transactions.
A cvv is usually three digits, but it can be four digits on some cards. Always check your card to determine the correct number of digits for your cvv.
The cvv is required anytime you cannot provide a merchant with a physical card, such as an online or phone purchase. This is because the cvv helps to verify that you have physical possession of the card and are authorized to make the purchase.