Ever wondered why that first bite of pizza tastes infinitely better than the fourth? It all boils down to the economic principles of total utility and marginal utility, concepts that govern our satisfaction and consumption patterns. Understanding these principles is key to unlocking insights into consumer behavior and economic decision-making.
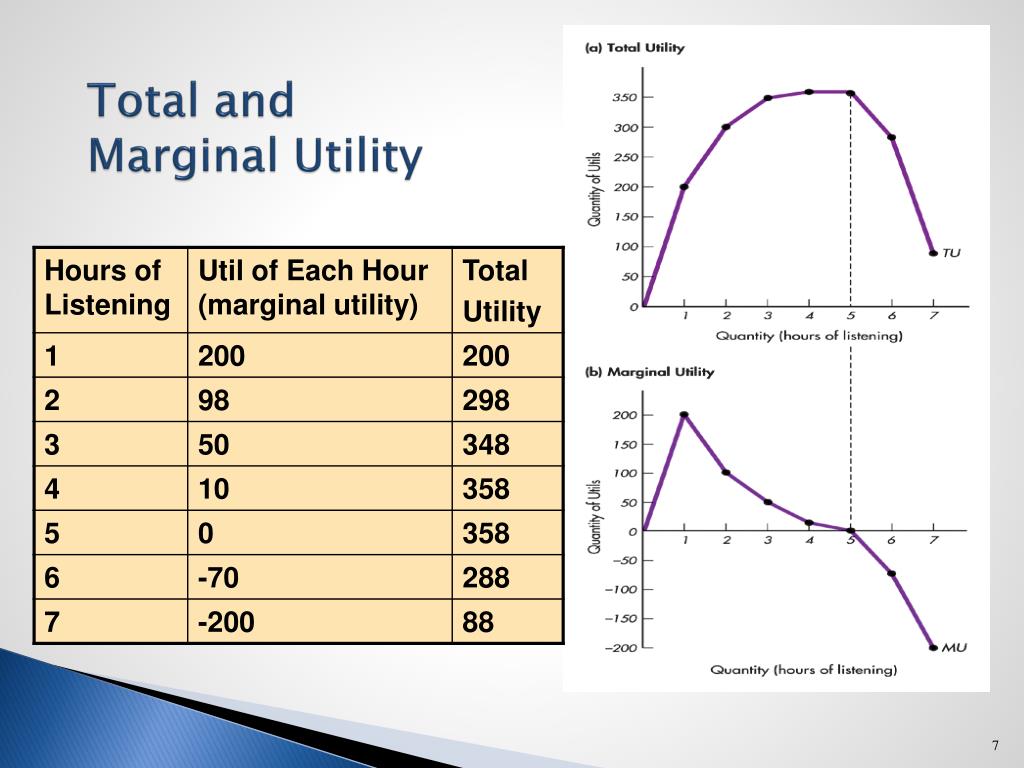
At the heart of these concepts lies the idea that as we consume more of something, our satisfaction from each additional unit tends to decrease. This is the essence of the law of diminishing marginal utility. Think about it: that first cup of coffee in the morning provides an incredible jolt and sense of alertness, while the third or fourth cup might just lead to jitters and a diminished sense of enjoyment. Economists are very interested in understanding exactly how both total utility and marginal utility interact.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Concept | Total Utility & Marginal Utility |
| Definition (Total Utility) | A conceptual measure of the overall satisfaction a consumer derives from consuming a specific quantity of a good, service, or activity. |
| Definition (Marginal Utility) | The additional satisfaction (or dissatisfaction) gained from consuming one more unit of a good, service, or activity. |
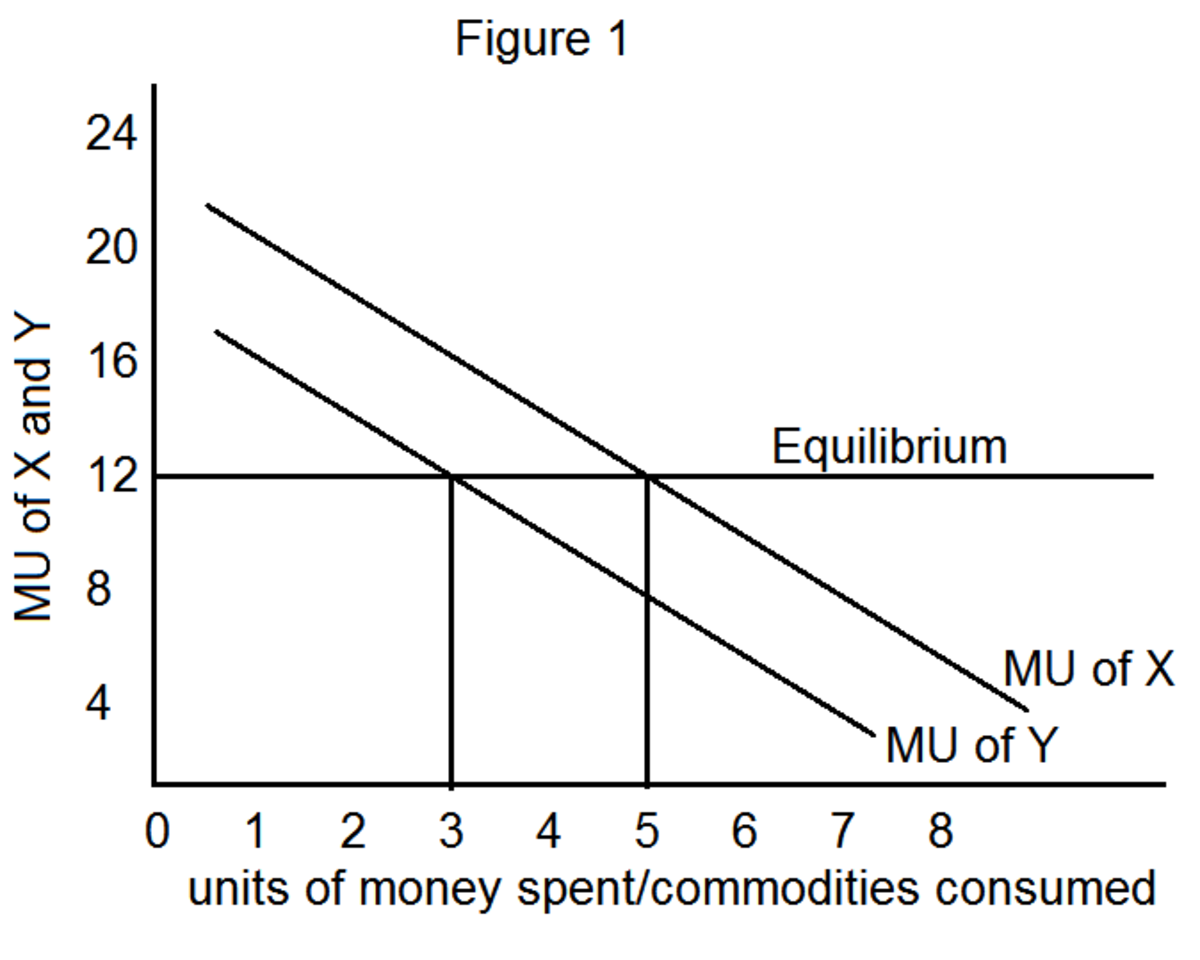
| Key Relationship | Total utility increases as long as marginal utility is positive; total utility is maximized when marginal utility is zero; total utility decreases when marginal utility is negative. |
| Diminishing Marginal Utility | The principle that as consumption of a good increases, the additional satisfaction derived from each additional unit tends to decrease. |
| Formula (Marginal Utility) | Marginal Utility = (Change in Total Utility) / (Change in Quantity Consumed) |
| Example | Ice cream consumption: The first scoop provides high satisfaction, subsequent scoops provide less and less satisfaction until eventually you are full and the extra scoop gives you no utility or even negative utility. |
| Relevance to Economics | Helps economists understand consumer behavior, demand curves, and optimal consumption choices. |
| Real-World Application | Pricing strategies, product design, marketing campaigns, and resource allocation. |
| Further Reading | Investopedia - Utility |