Is the water you're drinking truly as pure as you think? Ozonated water is emerging as a revolutionary solution in water purification and disinfection, promising a safer and healthier drinking experience. But what exactly is it, and how does it work?
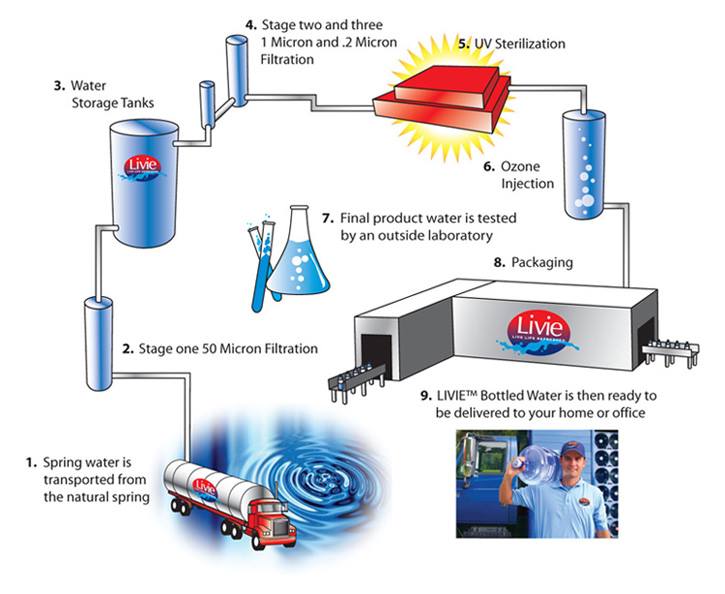
Ozonated water is created by infusing purified water with ozone gas, a process that harnesses ozone's potent disinfectant properties. Ozone, composed of three oxygen atoms (O3), is a naturally occurring gas and a powerful oxidant. The process involves continuously bubbling ozone gas into the water, allowing the ozone molecules to dissolve and react with any contaminants present. While ozone in its gaseous form may pose respiratory risks, when properly dissolved in water, it offers a range of benefits.
| Aspect | Ozonated Water |
|---|---|
| Definition | Water infused with ozone gas (O3) for disinfection and purification. |
| Production Method | Bubbling ozone gas into purified water. |
| Primary Use | Disinfection of water against bacteria, viruses, mold, and algae. |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly alternative to chemical treatments; ozone decomposes into oxygen, leaving no harmful residues. |
| Regulatory Approval | Classified as safe for water disinfection applications by the FDA in 1982. |
| Additional Applications | Disinfecting garbage disposal systems, grease traps, and reducing odors. |
| Bottled Water Industry | Extensively used to produce water of exceptional purity and stability. |
| Benefits | Potential therapeutic applications, strong oxidant properties, and effective water purification. |
| Considerations | Ozone in gaseous form can have respiratory consequences; the ozonation process must be properly controlled. |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, influenced by temperature and ionic strength. |
| History | First used in water treatment in the late 1800s; more widely used in Europe and Asia than in the United States. |
| Alternative Names | Ozone water |
| Molecular Composition | Enriched with ozone molecules. |
| Filtration Method | Environmentally friendly water filtration that doesn’t use chemicals as additives. |
| Oxidation | Oxidation of inorganic and organic pollutants. |
| Popularity | One of the most popular ways to use ozone in a therapeutic way. |
| Production | Made by running ozone gas through water. |
| Stability | The gas will readily degrade back to oxygen. |
![[ Ozonation ] Learn How Ozonation Process Works YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dB6Dxsxb8Og/maxresdefault.jpg)